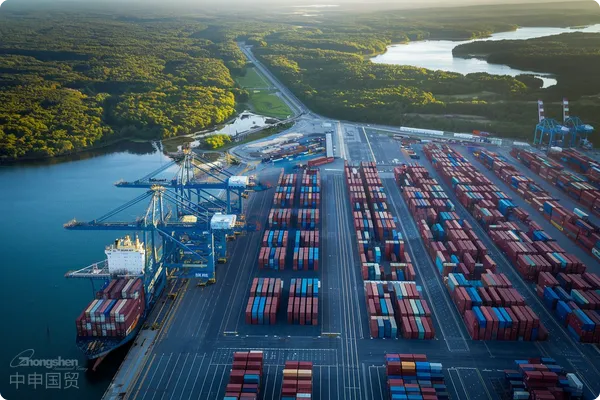
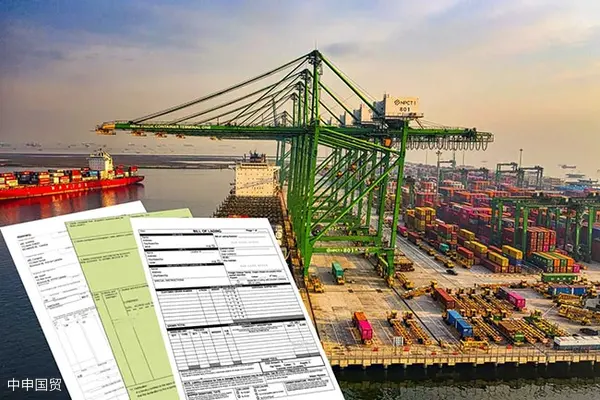
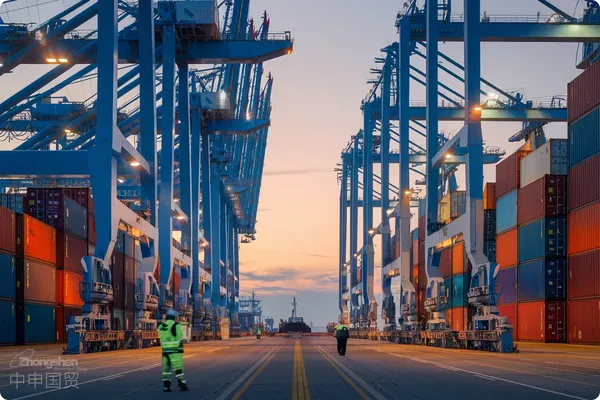
- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
Are you confused about the manifest fee and the pre - entry manifest fee when exporting goods? In fact, they have different scopes of application and charging purposes. Whether your destination is Australia or other countries, mastering the differences in these fees can help you avoid unnecessary expenses and ensure the smooth customs clearance of goods!
The mentioned manifest fee involves two different concepts: the general export manifest fee and the pre - entry manifest fee for specific countries/regions (such as AMS, ENS, AFR, etc.).
I. General export manifest fee
Manifest Fee
(a) Scope of application:The manifest fee applies to the declaration of any exported goods, regardless of the destination country or region of the goods. This is a basic operational requirement internationallyMaritime Transportationto ensure that the goods comply with customs declaration regulations before leaving the port.
(b) Purpose:The manifest is a cargo list submitted by the carrier (shipping company or freight forwarder) to the customs, listing the detailed information of all goods loaded on the ship. Manifest declaration is a key compliance step. Without a manifest, the goods cannot complete the arrival report, and subsequent customs clearance procedures cannot be carried out.
(c) Fee collection:In East China and North China, this fee is usually arranged and collected on behalf by the booking party; in South China, it is paid on behalf by the customs broker and is usually included in the customs declaration fee.
Manifest declaration process
Declaration requirements: Exported goods must declare the manifest to the port customs in advance and obtain the customs release permission. After the successful manifest declaration, the shipping company will obtain a customs arrival report number, which is an indispensable part of the subsequent customs clearance procedures.
II. Pre - entry manifest fee for specific countries
Pre - entry manifest fee (such as AMS, ENS, AFR)
(1) AMS (Automated Manifest System) in the United States:Applicable to goods exported to the United States. This system requires the shipping company or freight forwarder to declare the goods information to the US customs in advance before the goods are loaded on the ship to ensure the US customs supervision and risk assessment of imported goods.
(2) ENS (Entry Summary Declaration) in the EU:Applicable to goods exported to the EU. Similar to AMS, it requires the advance submission of goods information for review by the EU customs.
(3) AFR (Advance Filing Rules) in Japan:Applicable to goods exported to Japan, requiring the advance declaration of goods information.
(4) ACI (Advance Commercial Information) in Canada:Applicable to goods exported to Canada, requiring the advance submission of commercial information.
(5) Collection purpose:These fees are for the additional declaration requirements of specific countries or regions to meet the safety requirements of the customs of each destination country. This type of fee is usually related to the safety review and compliance inspection of the goods.
III. Conclusion
(1) General manifest fee:It is a regular fee that any exported goods need to pay, regardless of the destination of the goods. All exported goods need to complete the manifest declaration before loading, so this part of the fee needs to be paid.
(2) Pre - entry manifest fee:It is an additional fee for specific countries and is only applicable to goods exported to these countries. For example, the AMS fee is applicable to the United States, the ENS fee is applicable to the EU, and the AFR fee is applicable to Japan.
Therefore, the manifest fee charged by the freight forwarder is for the regular declaration fee in the export process, not the pre - entry manifest fee specific to certain countries. No matter which country you export to, complying with the declaration requirements and fee rules of each country can escort the safety of your goods.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023007705號-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912










